how to name ketones iupac Ketones naming name aldehydes nomenclature practice suffix chain
Hey there! Today, let’s dive into the fascinating world of organic chemistry and explore the naming conventions of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters. Understanding these naming rules will not only expand your knowledge in chemistry but also enable you to appreciate the complex structures and functions of these compounds. So, let’s get started!
Aldehydes
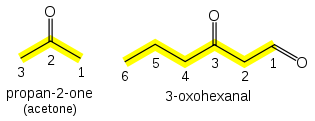 An aldehyde is a compound characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O), with a hydrogen atom (H) attached to the carbonyl carbon (C). The nomenclature of aldehydes follows a simple pattern. The parent chain is selected, and the suffix “-al” is added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For example, if the parent chain is pentane and the carbonyl group is present on the second carbon, the compound is named as “2-pentanal.”
An aldehyde is a compound characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group (C=O), with a hydrogen atom (H) attached to the carbonyl carbon (C). The nomenclature of aldehydes follows a simple pattern. The parent chain is selected, and the suffix “-al” is added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For example, if the parent chain is pentane and the carbonyl group is present on the second carbon, the compound is named as “2-pentanal.”
Ketones
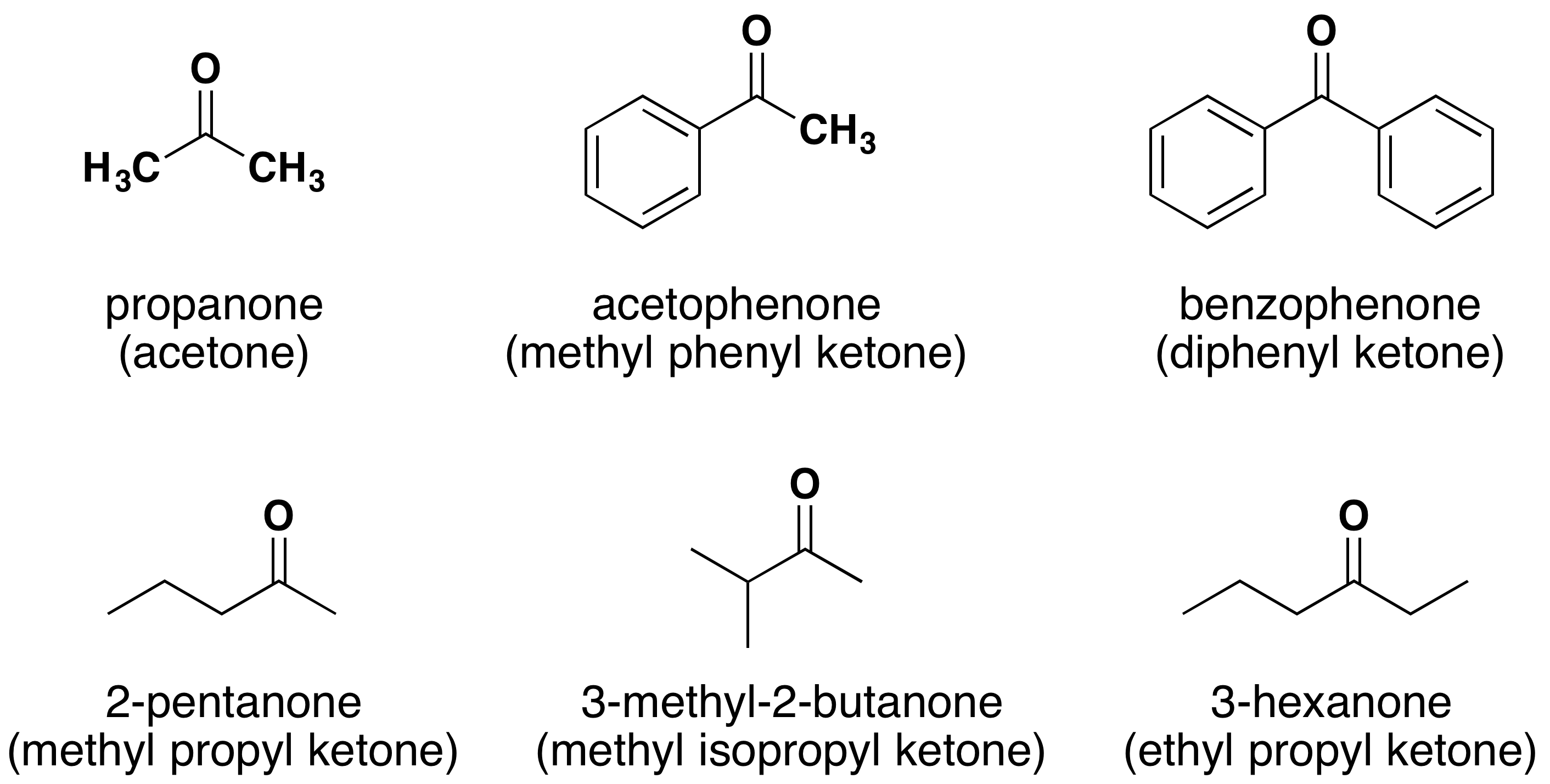 Similar to aldehydes, ketones also possess a carbonyl group. However, in ketones, both carbons attached to the carbonyl group are alkyl or aryl groups, rather than hydrogen. The naming of ketones involves identifying the parent chain, and the suffix “-one” is added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For instance, if the parent chain is hexane and the carbonyl group is present on the third carbon, the compound is named as “3-hexanone.”
Similar to aldehydes, ketones also possess a carbonyl group. However, in ketones, both carbons attached to the carbonyl group are alkyl or aryl groups, rather than hydrogen. The naming of ketones involves identifying the parent chain, and the suffix “-one” is added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For instance, if the parent chain is hexane and the carbonyl group is present on the third carbon, the compound is named as “3-hexanone.”
Carboxylic Acids
 Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain both a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the same carbon atom, known as the carboxyl group (-COOH). The nomenclature of carboxylic acids involves selecting the parent chain, generally the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carboxyl group. The suffix “-oic acid” is then added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For example, if the parent chain is propane, the compound is named as “propanoic acid.”
Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain both a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the same carbon atom, known as the carboxyl group (-COOH). The nomenclature of carboxylic acids involves selecting the parent chain, generally the longest continuous carbon chain containing the carboxyl group. The suffix “-oic acid” is then added to the stem name of the corresponding alkane. For example, if the parent chain is propane, the compound is named as “propanoic acid.”
Esters
 Esters are compounds derived from carboxylic acids by replacing the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxyl group with an alkoxy group (-OR). The naming of esters involves recognizing the parent carboxylic acid and the alcohol used to form the ester. The name of the alcohol becomes the first part of the ester name, followed by the name of the carboxylic acid with the “-oate” suffix. For instance, if the carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid and the alcohol is methanol, the ester formed is named as “methyl ethanoate.”
Esters are compounds derived from carboxylic acids by replacing the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the carboxyl group with an alkoxy group (-OR). The naming of esters involves recognizing the parent carboxylic acid and the alcohol used to form the ester. The name of the alcohol becomes the first part of the ester name, followed by the name of the carboxylic acid with the “-oate” suffix. For instance, if the carboxylic acid is ethanoic acid and the alcohol is methanol, the ester formed is named as “methyl ethanoate.”
Understanding the nomenclature of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters is crucial for communication within the field of organic chemistry. It allows chemists to precisely identify and describe these compounds, facilitating research, teaching, and collaboration. So, next time you encounter these compounds, remember the rules and ace their nomenclature!
Stay curious and keep exploring the captivating world of chemistry!
If you are searching about Naming Aldehydes and Ketones with Practice Problems - Chemistry Steps you’ve visit to the right page. We have 5 Images about Naming Aldehydes and Ketones with Practice Problems - Chemistry Steps like Nomenclature of Aldehydes & Ketones - Chemistry LibreTexts, Naming Aldehydes and Ketones with Practice Problems - Chemistry Steps and also 12.3: Naming aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, plus common. Read more:
Naming Aldehydes And Ketones With Practice Problems - Chemistry Steps
 www.chemistrysteps.comketones naming name aldehydes nomenclature practice suffix chain
www.chemistrysteps.comketones naming name aldehydes nomenclature practice suffix chain
Nomenclature Of Aldehydes & Ketones - Chemistry LibreTexts
 chem.libretexts.orgketones aldehydes nomenclature names common chemistry libretexts ketone naming iupac name organic carbonyl compounds molecule chem system acid
chem.libretexts.orgketones aldehydes nomenclature names common chemistry libretexts ketone naming iupac name organic carbonyl compounds molecule chem system acid
Name Ketones (IUPAC) | Science, Chemical-reactions, Organic Chemistry
 www.showme.comshowme
www.showme.comshowme
12.3: Naming Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, Esters, Plus Common
 chem.libretexts.orgiupac ketones ketone carboxylic acids esters naming aldehydes plus libretexts citizendium mellish
chem.libretexts.orgiupac ketones ketone carboxylic acids esters naming aldehydes plus libretexts citizendium mellish
Solved: A. Structures Of Some Aldehydes And Ketones 1) Dra… | Chegg.com
 www.chegg.comketones aldehydes structures solved
www.chegg.comketones aldehydes structures solved
Name ketones (iupac). Ketones aldehydes structures solved. Naming aldehydes and ketones with practice problems